In the intricate web of human health, the gut stands as a pivotal player, wielding significant influence over our overall well-being. Beyond its digestive duties, the gut harbors a vast ecosystem of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which plays a profound role in maintaining balance within our bodies. As science delves deeper into the intricacies of gut health, its importance emerges as a cornerstone of holistic wellness.
Understanding the Gut Microbiota
At the heart of gut health lies the diverse community of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms that populate our gastrointestinal tract. This intricate microbiome, comprising trillions of microorganisms, contributes to digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, metabolism, and even mental health.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and brain maintain a constant dialogue through the gut-brain axis, a complex communication network linking the central nervous system with the enteric nervous system of the gut. This bidirectional relationship underscores the profound impact of gut health on mental and emotional well-being, influencing mood, cognition, and stress response.
Immune Function and Inflammation
A healthy gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in regulating immune function and defending against pathogens. Imbalances in gut bacteria can compromise immune responses, leading to increased susceptibility to infections, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation.
Digestive Wellness
Optimal gut health is essential for efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. Imbalances in gut bacteria can disrupt digestive processes, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).



Supporting Gut Health
Nurturing gut health involves adopting lifestyle habits and dietary practices that promote a balanced microbiota and optimal digestive function. Incorporating the following strategies can support gut health:
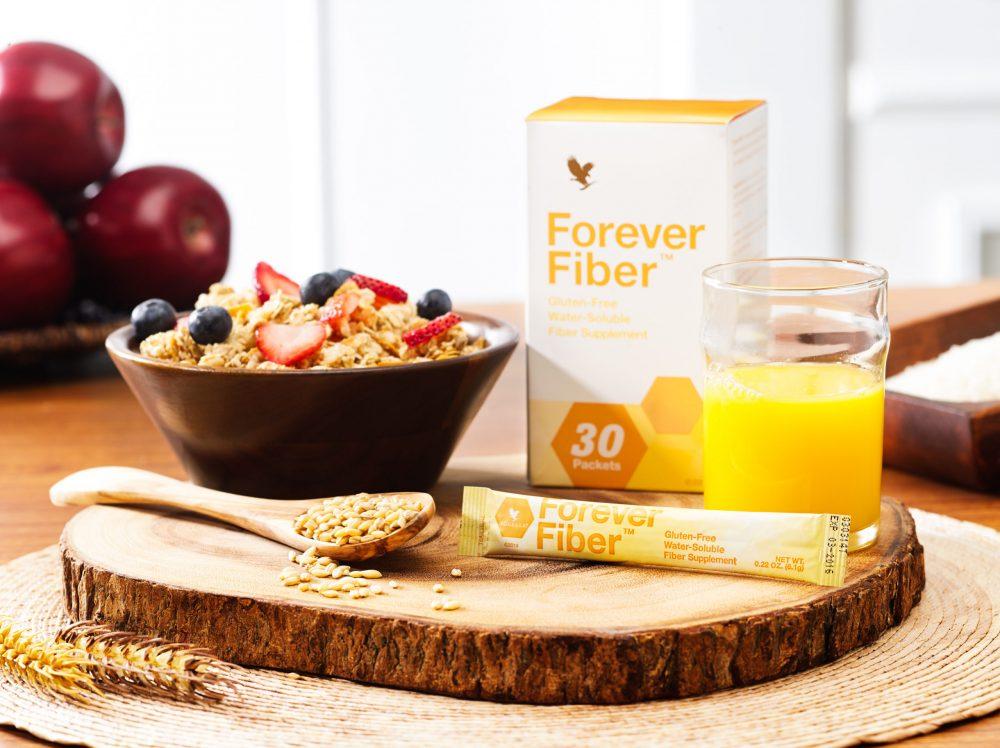
Fiber-Rich Diet: Consume a diverse array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts to provide prebiotic fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria. You can also supplement with Forever Fiber.
Probiotic Foods: Incorporate fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha into your diet to introduce beneficial probiotic bacteria. Supplement with Forever Active Pro-B.
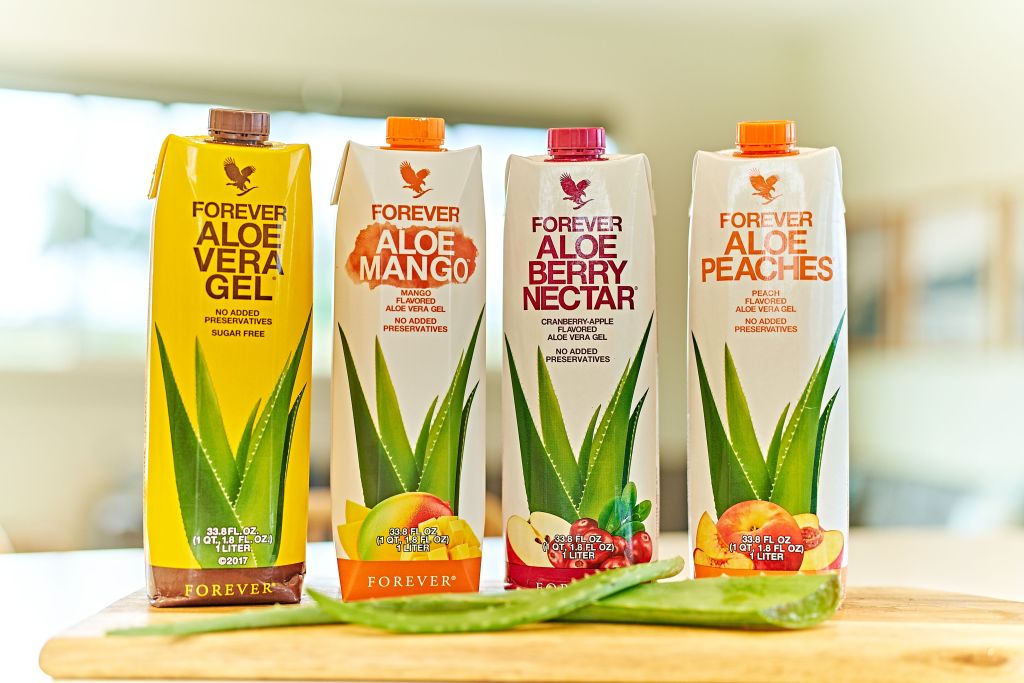
Aloe Vera Gel: Drink Aloe Vera Gel for better nutrient absorption and to keep gut bacteria in balance. It comes in 4 flavors: 1) Aloe Vera Gel (regular), 2) Aloe Berry Nectar, 3) Aloe Peaches, 4) Aloe Mango.
Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated to support digestion, nutrient absorption, and the movement of waste through the digestive tract.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and regular physical activity to support gut-brain balance.
Limiting Antibiotic Use: Use antibiotics judiciously and only as prescribed by a healthcare professional to minimize disruption to gut microbiota.
Avoiding Excessive Use of Antibacterial Products: Limit exposure to antibacterial soaps, sanitizers, and disinfectants, which can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Conclusion
In the quest for holistic wellness, nurturing gut health emerges as a fundamental pillar of self-care and preventive medicine. By honoring the intricate ecosystem within our digestive tracts and adopting mindful lifestyle practices, we can cultivate resilience, vitality, and balance from the inside out. As we embrace the symbiotic relationship between gut health and overall well-being, we embark on a journey of holistic transformation, empowering ourselves to thrive in mind, body, and spirit.
Do you have any questions or want to connect?
Discover more from Gut Health Matters
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




Pingback: You Are What You Eat—But It’s More Complicated Than You Think | Gut Health Matters